Tell if a Sparrow is Male or Female: A Quick Guide
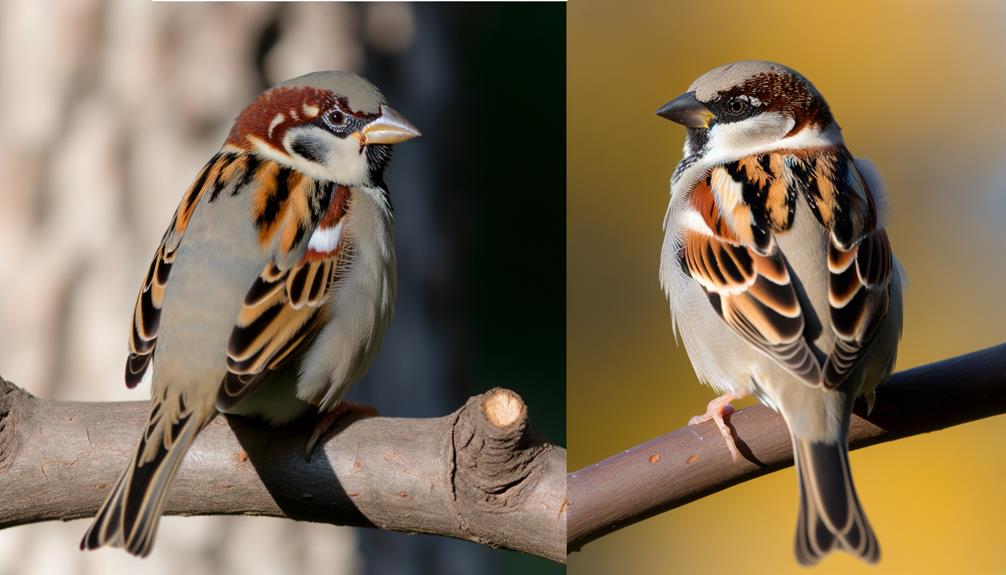
To tell if a sparrow is male or female, check their plumage and beak. Males have vibrant plumage with brighter patches on their crown, throat, and chest, and a darker beak, often turning black during breeding season.
They're also heavier with longer wings and a broader chest. Females exhibit duller coloration, lighter beak hues, and a more streamlined build.
Observing behavior helps too: males sing intricate calls and focus on nest building, while females refine nests and increase calls in response to males. For a deeper understanding of these fascinating birds, there's more to explore.

Key Takeaways
- Males have vibrant plumage with brighter patches on the crown, throat, and chest.
- Female sparrows have lighter, duller beak hues and more cryptic coloration.
- Males sing more frequently during mating season with intricate calls.
- Female sparrows have shorter wings and tail feathers with a more streamlined build.
- Males are heavier with longer wings, broader chest, and a robust build.
Plumage Differences
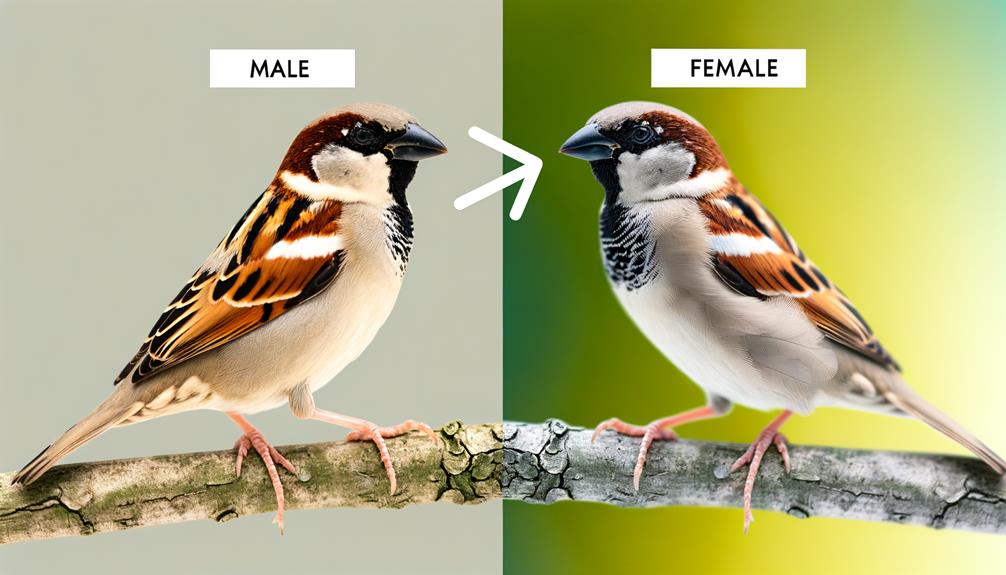
When identifying a sparrow's sex, observe the plumage: males generally exhibit more vibrant and distinct coloration compared to the more subdued and mottled tones of females. You'll notice the males often display brighter patches, particularly on the crown, throat, and chest. These areas can feature rich browns, blacks, and even some streaks of white, creating a striking contrast.
Females, in contrast, tend to have more cryptic coloration, which helps them blend into their surroundings. Their feathers are typically earth-toned, with less pronounced markings. Pay attention to these subtle differences in plumage when trying to determine the sex of a sparrow.
This precise observation can greatly aid in accurate identification, especially when assisting others in birdwatching or ornithological research.
Beak Color
You'll notice that male sparrows typically exhibit a darker, more vibrant beak coloration, especially during the breeding season.
Female sparrows, on the other hand, usually have lighter, duller beak hues.
Be aware that these color variations can fluctuate with seasonal changes, adding a layer of complexity to gender identification.
Male Beak Characteristics
In male sparrows, the beak typically exhibits a distinct black or dark gray coloration, which is a key identifier during the breeding season. This coloration is due to increased levels of melanin, a pigment that plays an essential role in sexual signaling.
You'll notice that outside the breeding season, the beak may appear more muted, shifting to a yellowish or lighter hue. Observing these changes can help you accurately determine the bird's sex.
Additionally, the beak's structure remains robust and conical, optimized for seed consumption. Keep in mind that lighting and environmental conditions might affect perceived coloration, so take multiple observations for accuracy.
Female Beak Features
Female sparrows generally exhibit beaks with a more consistent yellowish or light brown coloration, lacking the dramatic seasonal changes seen in males. When observing these birds, you'll notice that the female's beak maintains its hue throughout the year, aiding in identification.
The beak color can range from a pale yellow to a light brown, providing less contrast than the male's beak, which shifts seasonally. This subtlety requires careful attention to detail, especially when distinguishing between genders in the field. By focusing on these consistent color patterns, you can more accurately identify female sparrows.
Seasonal Color Changes
Observing the seasonal color shifts in a sparrow's beak provides crucial insights into distinguishing male sparrows, as their beak color undergoes a significant transformation from a drab brown or yellow in the non-breeding season to a bold black during the breeding period.
You'll observe that in the winter months, the male sparrow's beak seems unremarkable, blending in with the muted seasonal surroundings. As spring nears, the shift becomes noticeable; heightened melanin production leads to the beak darkening to a striking black. This change is connected to hormonal shifts linked to breeding readiness.
In contrast, females maintain a consistent beak color throughout the year, usually a yellow-brown shade. Monitoring these shifts aids in accurately identifying and comprehending sparrow behavior, assisting in effective bird care and support.
Size and Structure

One key difference between male and female sparrows is their size, with males typically being slightly larger and more robust in their overall structure. When observing sparrows, pay attention to their body mass and wing length, as these metrics can help distinguish between sexes. Male sparrows often have a more pronounced, muscular build and a broader chest. Female sparrows, on the other hand, are generally smaller and more streamlined, aiding in agility and nesting activities.
To assist your observations, refer to the table below:
| Trait | Male Sparrows | Female Sparrows |
|---|---|---|
| Body Mass | Heavier | Lighter |
| Wing Length | Longer | Shorter |
| Chest Width | Broader | Narrower |
| Build | Robust | Streamlined |
| Purpose | Territorial defense | Nesting and agility |
This comparison can enhance your ability to accurately identify sparrow gender.
Wing Patterns
In addition to size and structure, examining the wing patterns can provide valuable insights into determining the sex of a sparrow. Males typically exhibit more pronounced wing bars, which are the contrasting stripes across their wings. These wing bars are often brighter and more defined in males due to higher levels of melanin.
Females, on the other hand, tend to have subtler, less distinct wing patterns. You'll also notice that males have a more uniform coloration across their wings, whereas females might display a mottled appearance. Carefully observe the wing coverts and primary feathers; males usually show a cleaner, crisper differentiation between light and dark areas.
Tail Features
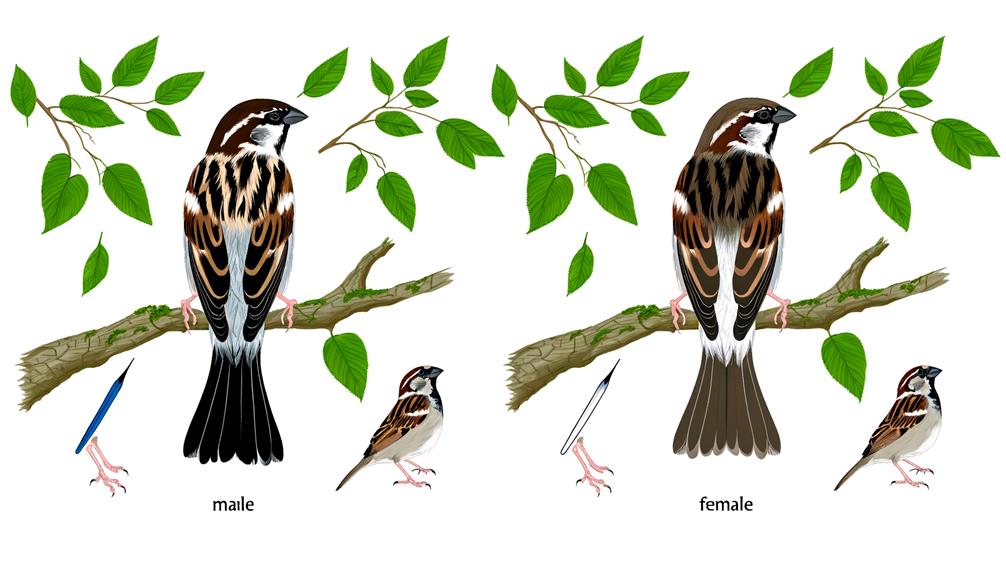
The tail feathers of a sparrow can reveal its sex through differences in length, shape, and coloration. Male sparrows often have longer tail feathers with a more pronounced, rounded tip. These feathers may also display a slightly richer coloration compared to females.
Female sparrows typically have shorter, more tapered tails with a more modest coloration, blending into their overall plumage. Examine the rectrices, the long, stiff feathers of the tail, for subtle clues. In many species, males exhibit more vibrant and distinct markings on these feathers.
Vocalizations
You can distinguish between male and female sparrows by observing their vocalizations. Males typically produce more complex song patterns, especially during the breeding season, to attract mates and defend territory.
Females, on the other hand, usually emit simpler calls and exhibit less vocal activity overall.
Song Patterns
Male sparrows often display distinct and intricate song patterns, which serve as a key indicator for differentiating them from females. These vocalizations, rich in frequency modulation and intricate sequences, are primarily used for territorial defense and attracting mates. You'll notice that males sing more frequently and with a wider variety compared to females.
Here's a quick reference table to help you identify these patterns:
| Aspect | Male Sparrows | Female Sparrows |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency of Songs | High | Low |
| Song Complexity | Complex with varied sequences | Simple, less varied |
| Purpose | Mate attraction, territory | Rarely for socio-communication |
Listening closely to these song patterns can significantly improve your ability to distinguish between male and female sparrows.
Call Differences
When identifying sparrows, notice that males and females exhibit distinct differences in their call vocalizations, which are shorter and less complex than their songs.
Male sparrows typically use sharper, more defined calls to establish territory and attract females. These calls often consist of a series of 'chip' or 'cheep' sounds with a consistent rhythm.
Females, on the other hand, emit softer, more variable calls, often in response to the males or to communicate with their chicks. Listen for these subtle variations—males' calls are usually more frequent and rhythmic, while females' calls are sporadic and subdued.
Seasonal Changes
Throughout the year, sparrows' vocalizations undergo noticeable changes in response to seasonal shifts. Spring and early summer often bring an increase in the frequency and complexity of their calls. Males, in particular, use these vocalizations to establish territory and attract mates. Females, on the other hand, may respond with shorter, simpler calls.
Here are three key changes in sparrow vocalizations due to seasonal shifts:
- Increased Frequency:
Males sing more frequently during mating season to attract females.
- Complexity:
Calls become more intricate to demonstrate fitness and establish dominance.
- Responsiveness:
Females' calls become more frequent in response to male songs.
Understanding these patterns helps you better distinguish between male and female sparrows.
Nesting Behavior
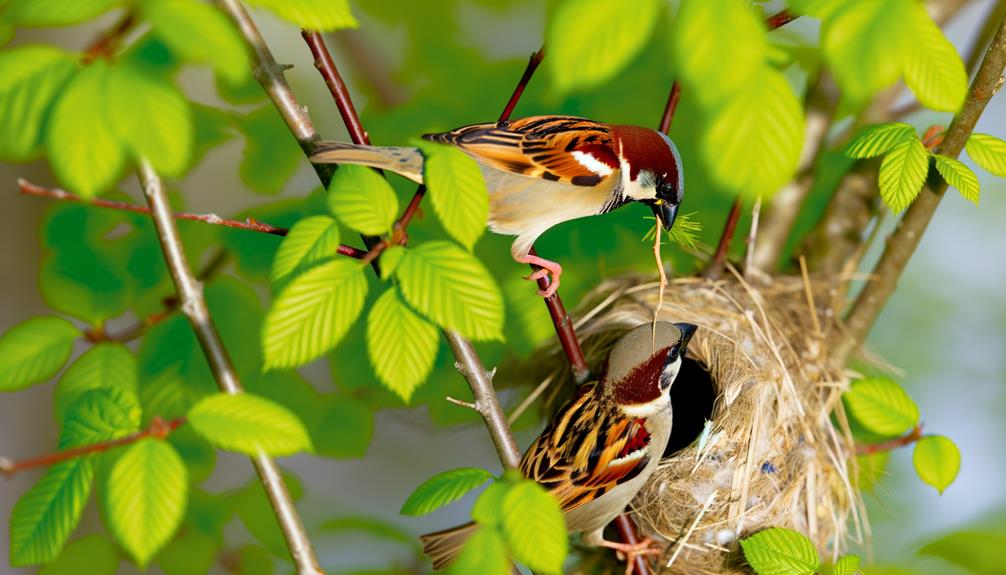

During the breeding season, sparrows exhibit distinct nesting behaviors that can help you identify males and females. Males often engage in nest building, selecting suitable sites and constructing the initial framework using grasses and twigs. You'll see them working tirelessly to attract a mate.
Females, on the other hand, focus on refining the nest, adding softer materials like feathers and lining the interior to secure a comfortable environment for egg incubation. Observing these behaviors, you can distinguish the male's role in structural construction from the female's involvement in nest completion.
Feeding Habits
Sparrows exhibit distinct sexual dimorphism in their feeding habits, with males often foraging in more exposed areas while females prefer safer, concealed locations. This behavior is driven by the need for females to minimize predation risk while they've a greater investment in reproduction.
When observing sparrows, you'll notice:
- Males: They tend to be more visible, feeding in open spaces where they can quickly spot predators.
- Females: They usually feed under cover, such as thick vegetation, to stay hidden from potential threats.
- Feeding Times: Males and females may also differ in their feeding times to reduce competition and increase survival chances.
Understanding these habits helps you support sparrows better by providing appropriate feeding spots and safe environments.
Seasonal Changes
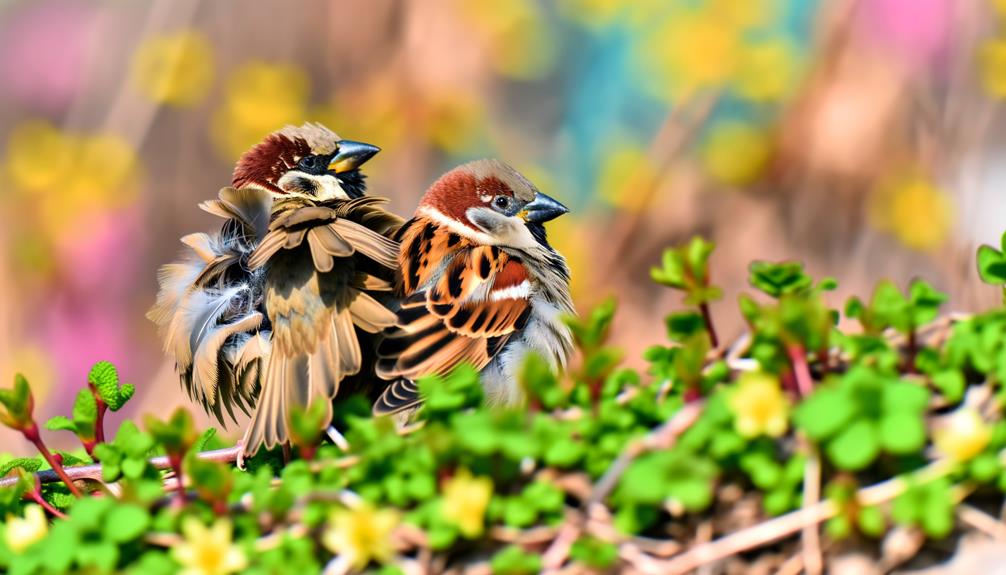

Not only do their feeding habits vary, but sparrows also exhibit distinct differences in plumage and behavior throughout the changing seasons. During the breeding season, males display vibrant, contrasting feathers to attract mates, while females have more subdued tones for camouflage. In non-breeding seasons, plumage becomes less vibrant in both genders.
Here's a detailed look at seasonal changes:
| Season | Observations |
|---|---|
| Breeding | Males: Bright plumage, active singing |
| Females: Subdued tones, nesting | |
| Non-Breeding | Males: Duller plumage, less singing |
| Females: Consistent camouflage | |
| Migration | Both: Increased feeding, flocking |
Understanding these seasonal variations can help you accurately identify the gender of sparrows, ultimately aiding in their conservation and study.
Conclusion
By observing plumage differences, noting beak color, comparing size and structure, examining wing patterns, and scrutinizing tail features, you'll reveal the secrets of sparrow sex identification.
Listen to distinct vocalizations, watch nesting behavior, observe feeding habits, and track seasonal changes. Through these detailed observations, you'll gain scientific accuracy and deepen your understanding of sparrows.
Recognize males by their vibrant markings and females by their subtler hues. It's a fascinating, rewarding endeavor, blending technical precision with natural beauty.






