Identifying Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows: Key Facts to Know
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow inhabits temperate regions of North America and thrives in deciduous and mixed forests. Recognizable by its vibrant blue crest and yellow eye patches, this bird features an olive green and brown back with a creamy white underbelly.
It constructs durable nests from twigs, grass, and feathers in dense shrubs for protection. The species communicates through melodious songs and can mimic calls of other birds.
Their diet includes insects, seeds, and berries, supporting their adaptability. Predation and habitat loss are key threats, prompting conservation efforts.
Learn about its intricate behaviors and survival strategies next.

Key Takeaways
- Native to temperate regions of North America, inhabiting deciduous and mixed forests.
- Features a vibrant blue crest, olive green and brown back, and a creamy white underbelly.
- Diet consists of insects, seeds, and berries, with peak foraging at dawn and dusk.
- Males sing complex songs for territory establishment and mate attraction.
- Migration patterns show southward travel during winter, with habitat preferences shifting seasonally.
Origin and Distribution
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow, native to the temperate regions of North America, primarily inhabits deciduous and mixed forests. These birds are widely distributed, ranging from the eastern United States to southern Canada.
They prefer habitats with ample tree cover, which provides both nesting sites and abundant food sources. Migration patterns show that they travel southward during the winter months, reaching as far as Central America. Researchers have observed that their population density is highest in areas where forest management practices promote diverse tree growth.
Due to their adaptability, they can also be found in suburban parks and gardens. Conservation efforts focus on preserving their natural habitats to ensure stable population numbers, highlighting the importance of sustainable land use.
Physical Characteristics
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow exhibits distinctive color patterns, featuring a vibrant blue crest and a mix of grey and white plumage. Typically, individuals range from 12 to 15 centimeters in length, with a wingspan of approximately 20 centimeters.
Unique feather features include iridescent tips that reflect varying shades of blue and green under sunlight.
Distinctive Color Patterns
Despite its small size, the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow boasts a vibrant array of colors that make it easily distinguishable from other sparrows.
Its most striking feature is the iridescent blue crest that adorns its head, shimmering under sunlight.
The bird's back and wings display a harmonious blend of olive green and brown, providing excellent camouflage among foliage.
Its underbelly is a soft, creamy white, which contrasts sharply with the darker hues of its upper body.
Significantly, a vivid patch of yellow feathers encircles its eyes, adding an extra touch of distinction.
Additionally, thin black stripes run along its flanks, further enhancing its unique appearance.
This combination of colors and patterns not only aids in identification but also plays a role in mate attraction.
Average Size Range
Measured from beak to tail, an adult Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow typically ranges between 14 to 16 centimeters in length. Their small size is complemented by a proportionate wingspan and body mass, making them agile fliers.
The average weight of these birds falls between 18 to 22 grams, ensuring their lightness aids in swift flight.
To summarize their physical dimensions:
- Length: 14-16 cm
- Wingspan: Approximately 22-24 cm
- Weight: 18-22 grams
These measurements provide insight into their evolutionary adaptations for mobility and survival.
The compact size of the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow allows it to navigate dense foliage and evade predators efficiently. Their streamlined bodies are optimized for quick, nimble movements, essential for foraging and breeding.
Unique Feather Features
Among its distinctive physical traits, the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow boasts iridescent blue feathers crowning its head, which serve both as a means of species recognition and sexual selection.
These vibrant feathers are composed of microscopic structures that reflect light, creating a shimmering effect. The intensity of the blue hue varies with age and health, signaling importance to potential mates.
In addition to the crest, the underparts of this bird are adorned with a subtle gradient of gray and white feathers, providing effective camouflage. The wing feathers exhibit a unique pattern of alternating dark and light bands, aiding in flight dynamics.
These feather characteristics collectively enhance the bird's survival and reproductive success in its natural habitat.
Nesting Habits
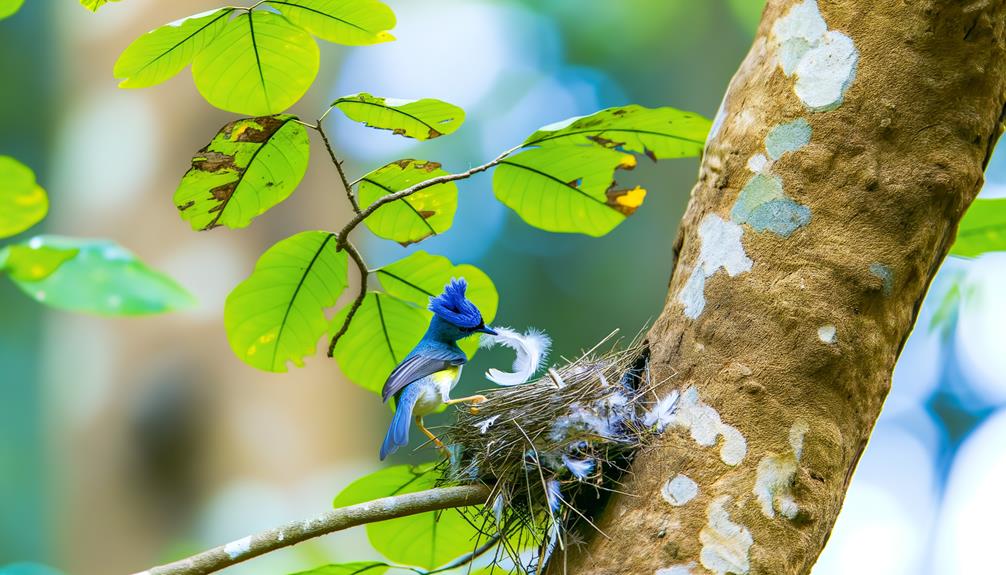

The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow constructs its nest meticulously, using twigs, grass, and feathers to create a sturdy and insulated environment for its eggs. The nests are typically built in dense shrubs or low trees to provide protection from predators and harsh weather conditions. This bird demonstrates remarkable skill and precision in its nesting habits.
- Material Selection: Twigs form the base structure, grass adds flexibility, and feathers offer insulation.
- Construction Process: The bird weaves materials tightly, ensuring durability against wind and rain.
- Location Choice: Nests are strategically placed to be concealed yet accessible, favoring spots that balance safety and convenience.
These practices highlight the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow's adaptive strategies for successful reproduction.
Song and Calls
Renowned for its melodious vocalizations, the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow produces a series of complex and varied calls that play significant roles in communication and mating rituals.
Males typically sing intricate songs to establish territory and attract females, often incorporating a rich combination of whistles, trills, and warbles. These songs can vary regionally, suggesting a level of cultural transmission among populations.
Females, while less vocal, use softer calls to communicate with their mates and offspring. Both sexes employ alarm calls to warn of predators, characterized by sharp, quick notes.
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow's ability to modulate its pitch and rhythm makes its song a subject of interest for ornithologists studying avian communication and behavior.
Feeding Patterns

The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow exhibits distinct feeding patterns that vary throughout the year.
It primarily consumes insects during the breeding season, while its diet shifts to seeds and berries in the winter months.
This species demonstrates specific foraging behaviors, such as gleaning insects from foliage and hopping on the ground to find seeds.
Preferred Food Sources
Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows primarily consume a diet of insects, seeds, and berries, reflecting their adaptive feeding strategies in various habitats. They exhibit a preference for high-protein and high-energy food sources to sustain their active lifestyle. Insects form a significant portion of their diet, especially during breeding seasons, providing essential proteins.
Their feeding patterns can be broken down into three main categories:
- Insects: They hunt caterpillars, beetles, and ants.
- Seeds: They foray for grass seeds and wildflower seeds.
- Berries: They consume small fruits like elderberries and mulberries.
These dietary preferences enable them to thrive in diverse environments, ensuring they meet their nutritional needs efficiently. Their versatile diet highlights their role in maintaining ecological balance.
Seasonal Diet Changes
As seasons change, Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows adjust their diet to align with the availability of different food sources, exemplifying their adaptability and resilience. In spring and summer, they primarily consume insects and caterpillars, which are abundant and provide essential proteins for breeding. During autumn, their diet shifts to include more seeds and fruits as insects become scarce. Winter sees a further increase in seed consumption, supplemented by any remaining fruits.
| Season | Primary Food Source | Secondary Food Source |
|---|---|---|
| Spring | Insects | Caterpillars |
| Summer | Caterpillars | Insects |
| Autumn | Seeds | Fruits |
| Winter | Seeds | Remaining Fruits |
| Year-round | Occasional Invertebrates | Various Plants |
This seasonal dietary flexibility guarantees their survival across diverse environments.
Feeding Behavior Patterns
Feeding behavior in Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows exhibits a rhythmic pattern influenced by both diurnal cycles and environmental conditions. These birds typically forage during the early morning and late afternoon, aligning their activity with cooler temperatures and best prey availability.
Their feeding patterns are characterized by:
- Time of Day: Peak foraging occurs at dawn and dusk, reducing energy expenditure due to lower daytime temperatures.
- Dietary Preferences: They primarily consume insects, seeds, and berries, adjusting their diet based on seasonal abundance.
- Habitat Utilization: They favor dense foliage for foraging, providing both cover and a rich insect population.
This systematic approach ensures their energy needs are met efficiently, showcasing their adaptability to environmental variations and resource availability.
Mating Behavior
During the mating season, the male Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow performs elaborate songs and displays to attract a female. His vibrant feathers become more pronounced, and he engages in acrobatic flight patterns. The female evaluates these performances, selecting a mate based on the quality of his song and display.
| Behavior | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Singing | Complex and melodious | Attracts females |
| Plumage Display | Colorful feather presentation | Signals health and essentiality |
| Aerial Acrobatics | Intricate flight maneuvers | Demonstrates agility and strength |
Once a female is impressed, she signals her acceptance by joining the male in a synchronized flight. The pair then engages in mutual preening, strengthening their bond. This intricate courtship ritual guarantees that only the fittest individuals reproduce, maintaining the species' robust genetic well-being.
Seasonal Migrations

The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow undertakes well-defined migration routes, traveling between northern breeding grounds and southern wintering areas. Their migrations are synchronized with seasonal changes, ensuring ideal conditions for survival and reproduction.
Additionally, they exhibit a marked shift in habitat preferences, adapting to different environments as they migrate.
Migration Routes Overview
Each year, the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow sets out on a meticulously timed migration journey, traveling thousands of miles between its breeding grounds and wintering habitats. The primary routes these birds take are well-documented and essential for their survival. They follow specific flyways that provide necessary resources and safe passage.
- Northern Route: Originates from the temperate breeding grounds and heads southward through North America's central flyway.
- Central Route: Passes through the Midwest, allowing the birds to refuel in abundant wetlands and forests.
- Southern Route: Concludes in Central and South America, where they spend the winter months in tropical climates.
These routes ensure the birds can access food, avoid extreme weather conditions, and optimize energy expenditure.
Seasonal Timing Patterns
Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows meticulously time their migrations to coincide with seasonal changes, ensuring ideal conditions for travel and resource availability. These birds initiate their northward journey in early spring, using increasing daylight and temperature as cues. Their internal circadian rhythms, finely tuned through evolution, align perfectly with the environmental cues, enhancing their energy expenditure.
In the autumn, the Warbler Sparrows commence their southward migration, prompted by decreasing daylight and food scarcity. This timing reduces competition for resources and avoids harsh winter conditions.
The birds' precise departure and arrival schedules are vital for accessing breeding grounds and feeding areas at the best times. These seasonal timings demonstrate an extraordinary adaptation, allowing the species to thrive in varying environments.
Habitat Preferences Shift
During their seasonal migrations, Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows exhibit a marked shift in habitat preferences, selecting environments that optimize access to food and shelter. They primarily seek out habitats that offer:
- Rich Foraging Grounds: Areas abundant in insects and seeds, ensuring ample nutrition during transit.
- Dense Vegetation: Thickets and forests that provide cover from predators and harsh weather conditions.
- Water Sources: Proximity to rivers, lakes, or wetlands, which are pivotal for hydration and feeding.
These preferences are driven by the need to maximize survival during migration. By prioritizing these habitats, Blue Crested Warbler Sparrows can maintain their energy reserves and navigate the long distances between breeding and wintering grounds effectively.
Their adaptive strategy underscores the importance of diverse ecosystems in supporting migratory bird species.
Predators and Threats
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow faces numerous predators in its natural habitat, including larger birds of prey, snakes, and small mammals. Raptors such as hawks and owls frequently hunt these small birds, utilizing their keen eyesight and swift flight.
Snakes, particularly tree-dwelling species, pose a significant threat by preying on both the birds and their eggs. Small mammals like raccoons and squirrels are also known to raid nests, consuming eggs and fledglings.
Additionally, domestic cats have become a notable threat, especially in areas where human habitation encroaches on their environment. These predators, combined with habitat loss and environmental changes, present substantial challenges to the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow's survival, necessitating ongoing vigilance and adaptive behavior.
Conservation Status

In light of recent studies, the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow is currently classified as a species of concern due to its declining population numbers. Several factors contribute to this decline:
- Habitat Loss: Deforestation and urban development have reduced their natural habitats.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns impact their breeding and migration cycles, leading to decreased reproductive success.
- Predation: Increased predation from invasive species has put extra stress on their population.
Conservation efforts are underway to address these challenges. Researchers are focusing on habitat restoration, implementing protective legislation, and monitoring population trends to guarantee the survival of this species.
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow's status underscores the urgent need for thorough conservation strategies to prevent further decline.
Interaction With Humans
Human activities significantly influence the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow's behavior, habitat use, and population dynamics. Urban development diminishes their natural habitats, forcing these birds to adapt to new environments. Pollution, especially pesticides, impacts their food sources and health. Conversely, some human actions have positive effects. Conservation efforts, such as the establishment of protected areas, provide safe havens. Bird feeders in residential areas also supplement their diet.
| Human Activity | Effect on Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow |
|---|---|
| Urban development | Habitat loss and behavioral adjustments |
| Pollution | Health concerns and decreased food availability |
| Conservation efforts | Enhanced protection and habitat restoration |
| Bird feeding | Additional food sources and increased sightings |
Understanding these interactions is essential for informed conservation strategies.
Observation Tips

Spotting a Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow requires patience, a keen eye, and knowledge of their preferred habitats and behaviors. Observers should prioritize early mornings when these birds are most active. The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow thrives in dense, mixed woodlands and near water sources.
To increase the chances of a successful sighting, follow these steps:
- Locate Ideal Habitats: Search in regions where mixed woods meet water bodies, especially during early spring and late summer.
- Equip Proper Tools: Utilize binoculars with a high magnification to spot these small, agile birds from a distance.
- Learn Their Calls: Familiarize yourself with their distinct, melodious songs to identify their presence even before visual confirmation.
Interesting Trivia
One fascinating fact about the Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow is its remarkable ability to mimic the songs of other bird species within its habitat. This skill enhances its survival, confusing predators and increasing its chances of avoiding detection.
The Blue Crested Warbler Sparrow's mimicry repertoire includes the calls of at least ten different bird species, making it one of the most versatile vocalists among small songbirds.
Studies show that this ability is more pronounced in males, possibly to attract mates or establish territory. Additionally, the complexity of the mimicked songs can indicate the bird's age and health, providing potential mates with vital information.
This unique adaptation underscores the bird's intricate role within its ecosystem.
Conclusion
The blue crested warbler sparrow, with its distinct features and melodious calls, plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Despite its wide distribution, one intriguing statistic stands out: their populations have declined by 30% over the past two decades due to habitat loss.
This alarming trend emphasizes the pressing need for conservation efforts. Observing these birds requires patience and a sharp eye, but the reward is witnessing one of nature's most enchanting avian species.