What Is the Meaning of a Flock of Sparrows in Terms of More Value?
A flock of sparrows signifies more than just communal behavior; their intricate social hierarchies and sophisticated communication patterns impart immense importance. Sparrows symbolize freedom, resilience, and protection across Asian, European, and Native American cultures.
Their ecological role includes pest control and seed dispersal, contributing significantly to biodiversity. Vocalizations within flocks facilitate territory establishment, mate attraction, and coordinated actions, crucial for survival.
Conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration, emphasizing their societal importance. Observing their behavior reveals deeper insights into the complex interplay of ecology and culture; interested individuals can explore further to grasp the layers of meaning they offer.

Key Takeaways
- A flock of sparrows symbolizes community, cooperation, and social bonds, emphasizing the value of working together.
- Sparrows in a group represent resilience and collective strength, highlighting the importance of unity in facing challenges.
- The presence of a sparrow flock signifies ecological health and biodiversity, indicating a balanced ecosystem.
- Sparrows in numbers enhance pest control, contributing to agricultural productivity and reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
- Flocks of sparrows demonstrate intricate social structures and communication skills, showcasing advanced social behaviors and adaptability.
Historical Significance of Sparrows

Throughout history, sparrows have played an important role in various cultures and ecosystems, often symbolizing freedom, simplicity, and resilience. These small passerine birds, belonging to the family Passeridae, have thrived in diverse habitats, from urban environments to rural landscapes. They exhibit remarkable adaptability, often nesting in man-made structures.
Their diet primarily consists of seeds and insects, making them essential for pest control and seed dispersal. Observations have shown that sparrows engage in complex social behaviors, including communal roosting and cooperative breeding. Their vocalizations, characterized by a series of chirps and calls, facilitate communication within flocks.
Despite their small size, sparrows' ecological impact is substantial, contributing to the balance of various ecosystems and highlighting their historical significance.
Symbolism in Different Cultures
Different cultures attribute diverse symbolic meanings to sparrows, reflecting their unique worldviews and traditions.
Asian cultures often view sparrows as symbols of joy and community, while European folklore frequently associates them with protection and fortune.
In Native American beliefs, sparrows are considered messengers carrying important spiritual insights.
Asian Cultural Significance
In many Asian cultures, sparrows symbolize joy, community, and protection, reflecting their sociable nature and intricate behaviors. These small passerine birds are often observed in large flocks, demonstrating complex social structures and cooperative interactions.
Their presence is imbued with auspicious meanings; in Chinese culture, sparrows are considered harbingers of happiness and prosperity. Japanese traditions also view these birds as protectors against misfortune. The sparrow's adaptive foraging strategies and nesting habits showcase resilience and resourcefulness, traits highly valued in Asian societies.
Additionally, their vocalizations, characterized by rapid, melodious chirping, are believed to bring positive energy and harmony. The cultural significance of sparrows in Asia underscores their role as symbols of collective well-being and mutual support.
European Folklore Insights
While sparrows hold significant meanings in Asian cultures, European folklore also imbues these birds with rich symbolic value, often associating them with themes of love, loyalty, and the soul's journey.
In medieval European traditions, sparrows were perceived as the souls of deceased individuals, guiding the living through their presence. In Christian iconography, the sparrow embodies God's care for the smallest and seemingly insignificant creatures, emphasizing divine providence.
Additionally, in British folklore, a sparrow entering a home portends good luck or the arrival of a visitor. These interpretations highlight the sparrow's role as a messenger and symbol of spiritual interconnectedness.
The nuanced symbolism of sparrows in European folklore underscores their multifaceted significance across various cultural narratives.
Native American Beliefs
How do Native American cultures imbue sparrows with profound symbolic meanings, often linking them to themes of protection, community, and ancestral guidance?
In many tribes, sparrows are considered messengers from the ancestors, providing spiritual guidance. Their communal nature symbolizes unity and cooperation, essential values in tribal societies.
Specific legends mention sparrows as protectors, warning of impending danger. The Cherokee, for instance, regard sparrows as guardians of crops, invoking their presence to ward off pests.
Ornithological studies within these cultures also highlight the sparrow's role in maintaining ecological balance, further enhancing their symbolic status.
Therefore, through intricate mythologies and ecological observations, Native American beliefs grant sparrows a revered status, encapsulating protection, community, and ancestral wisdom.
Social Structure of Flocks
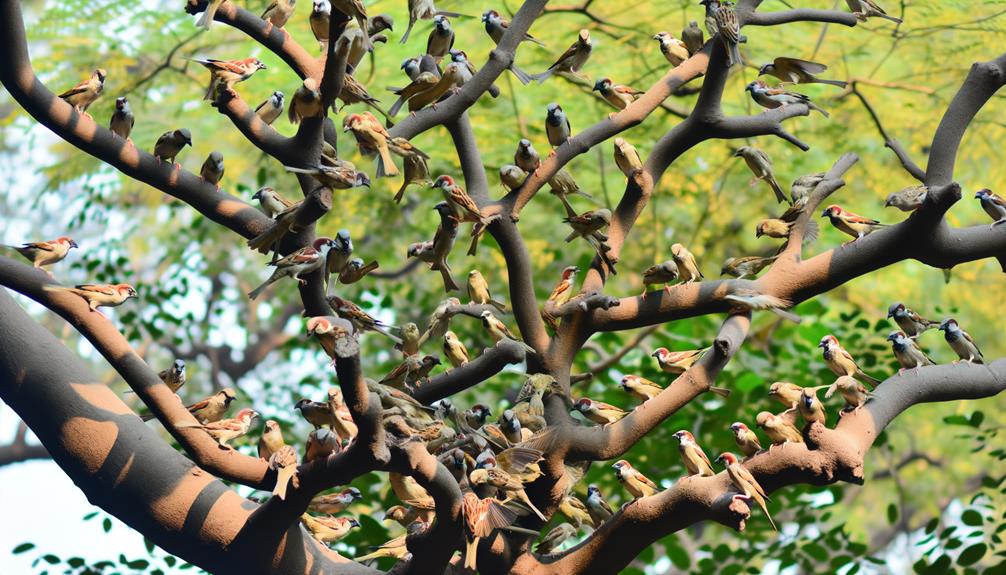
Researchers have observed that sparrow flocks exhibit complex social hierarchies, characterized by established roles and intricate communication networks. Dominant individuals typically occupy higher ranks, gaining priority access to resources like food and nesting sites. Subordinate sparrows defer to these dominant birds, which reduces conflict within the flock.
Juveniles and newcomers often start at the lowest ranks but can ascend through displays of strength or strategic alliances. Flocks also form kin-based subgroups, bolstering cooperative behaviors such as communal feeding and predator vigilance. This social structure enhances the flock's overall survival, as each member's role contributes to collective efficiency.
Communication Among Sparrows
Sparrows exhibit complex communication behaviors through social interaction patterns, vocalizations, and various signals.
Their vocal repertoire includes distinct calls and songs that facilitate group coordination and convey critical information about threats and resources.
Additionally, sparrows utilize visual cues and body language to reinforce social bonds and maintain flock cohesion.
Social Interaction Patterns
Although often overlooked, vocalizations among sparrows exhibit a complex array of calls and songs that serve critical roles in establishing territory, attracting mates, and coordinating group behaviors.
Beyond vocalizations, sparrows engage in various social interaction patterns that enhance their survival and reproductive success. Dominance hierarchies emerge within flocks, dictating access to resources like food and nesting sites. These hierarchies are established through subtle physical displays, such as posturing and pecking. Mutual preening, known as allopreening, strengthens social bonds and reduces stress.
Coordinated flight patterns, or murmurations, facilitate predator avoidance and efficient foraging. By maintaining intricate social networks, sparrows optimize their collective vigilance and resource acquisition, exemplifying the importance of social structures in avian species.
Vocalization and Signals
Intricate vocalizations and signals among sparrows serve as a sophisticated communication system essential for their survival and social organization. These birds utilize a complex array of sounds and gestures to convey information about food sources, predator presence, and mating readiness.
| Vocalization Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Contact Calls | Maintain group cohesion |
| Alarm Calls | Warn of predators |
| Mate Attraction | Signal reproductive availability |
| Juvenile Begging | Request food from parents |
| Territorial Songs | Establish and defend territory |
Each vocalization type exhibits unique frequency patterns, durations, and volumes, allowing other sparrows to interpret the message accurately. For instance, alarm calls are typically short and sharp, designed to elicit immediate attention. Understanding these communication mechanisms highlights the intricate social structures and survival tactics employed by sparrows.
Group Coordination Dynamics
Effective group coordination in sparrow flocks hinges on their ability to rapidly exchange information through a blend of vocal and visual signals, guaranteeing synchronized actions and enhanced survival. Sparrows employ a sophisticated communication system to navigate challenges and optimize foraging.
- Vocal Signals: Chirps and calls convey warnings about predators or signals to regroup, promoting collective vigilance.
- Visual Cues: Wing and tail movements serve as immediate, non-verbal signals to change direction or altitude swiftly.
- Proxemics: Maintaining ideal spacing within the flock reduces collision risks and ensures smooth motion, particularly during evasive maneuvers.
Understanding these dynamics showcases sparrows' advanced social structures and adaptive behaviors. Their coordination mechanisms not only strengthen survival but also highlight the intricate balance within avian communities.
Sparrows in Literature and Art

How frequently have sparrows appeared as symbols of freedom and fragility in literature and art?
Sparrows are ubiquitous in literary and artistic works, often representing delicate beauty and existential liberty. In literary contexts, authors like John Keats and William Blake have utilized sparrows to evoke themes of ephemeral existence and emotional resilience.
Art historically mirrors this symbolism; paintings from the Romantic era frequently depict sparrows in natural settings, emphasizing their vulnerability and unbounded flight.
Technically, their diminutive size and social behavior make them ideal for expressing complex human emotions succinctly. This avian imagery functions as a potent metaphor, capturing the essence of human experiences through a biological lens.
Such representations enrich our cultural and scientific understanding of sparrows.
Ecological Roles of Sparrows
Sparrows play crucial ecological roles in their habitats. They aid in plant propagation and habitat regeneration through seed dispersal. This helps in maintaining ecological balance by controlling pest populations through insect predation. Sparrows also contribute to biodiversity by supporting various trophic interactions within ecosystems.
These small birds are essential for the health and functioning of their ecosystems, playing a significant role in sustaining plant life, controlling pests, and promoting biodiversity.
Seed Dispersal Agents
Many species of sparrows play an essential role in their ecosystems as seed dispersal agents, aiding in the propagation of various plant species. These small but mighty birds consume seeds from a range of plants and later excrete them in different locations, facilitating plant growth.
Observations reveal that sparrows help maintain biodiversity and support ecosystem stability.
Key ways sparrows contribute to seed dispersal include:
- Foraging Behavior: Sparrows' foraging habits allow them to transport seeds over considerable distances.
- Dietary Preferences: Their varied diet means they disperse seeds from many plant species.
- Movement Patterns: Seasonal migrations and daily movements expand the range of seed dispersal.
Pest Population Control
Interestingly, these small birds play a crucial role in regulating pest populations by preying on insects, thereby contributing to the health of their ecosystems. Sparrows exhibit a particular fondness for consuming aphids, caterpillars, and beetles, which are common agricultural pests.
By targeting these insects, sparrows effectively reduce the need for chemical pesticides, promoting a more balanced and sustainable agricultural environment. Their feeding behavior supports integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, enhancing crop yields and reducing economic losses.
Observations reveal that sparrows' predation directly influences pest population dynamics, demonstrating a natural form of biological control. This understanding of the ecological role of sparrows in pest population control underscores their importance in maintaining ecosystem stability and agricultural productivity.
Biodiversity Enhancement
Through their diverse ecological roles, sparrows greatly contribute to biodiversity enhancement by facilitating seed dispersal, providing prey for predators, and participating in nutrient cycling. Their activities enrich ecosystems in several ways:
- Seed Dispersal: Sparrows consume various seeds and later excrete them in different locations, promoting plant diversity and forest regeneration.
- Prey for Predators: Sparrows are integral to food webs, serving as prey for birds of prey, mammals, and reptiles, thereby supporting predator populations.
- Nutrient Cycling: By foraging and nesting, sparrows help decompose organic material, enhancing soil fertility and promoting plant growth.
These roles highlight the significance of sparrows in maintaining healthy, balanced ecosystems, emphasizing the need for their conservation.
Impact on Pest Control

Noteworthy, a group of sparrows can greatly decrease pest populations by consuming large quantities of insects and larvae. Their diet mainly consists of aphids, caterpillars, and beetles, which are common agricultural pests. With their sharp foraging abilities, sparrows can effectively lessen the damage inflicted on crops, thereby reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
This natural pest control method promotes ecological balance and enhances crop yields. Observations indicate that a single sparrow can consume up to 850 insects daily, showcasing their efficiency in pest reduction.
Additionally, by targeting various pest life stages, from eggs to adults, sparrows contribute to a sustainable form of pest management that benefits both small-scale gardens and large agricultural fields.
Adaptability to Urban Environments
Sparrows exhibit remarkable adaptability to urban environments, thriving amidst the concrete jungles by exploiting diverse food sources and nesting opportunities. Their success in cities is attributed to several factors:
- Dietary Flexibility: Sparrows consume a wide range of foods, from insects to human scraps, ensuring a steady food supply.
- Nesting Versatility: They utilize various urban structures, such as buildings and streetlights, for nesting, capitalizing on readily available materials.
- Reduced Predation: Urban areas often have fewer natural predators, providing a safer habitat for sparrows.
These birds demonstrate behavioral plasticity, altering their feeding and nesting habits to suit the urban landscape. Their ability to adapt to human-altered environments underscores their resilience and ecological significance within urban ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts Worldwide

While urban adaptability highlights their resilience, global conservation efforts aim to address the declining populations of sparrows in both rural and urban environments.
Conservationists employ habitat restoration, focusing on native vegetation to provide essential food sources and nesting sites. They're also implementing measures to mitigate pesticide use, which negatively impacts sparrow populations. Additionally, citizen science projects like bird counts help track population trends and inform conservation strategies.
Urban planning is increasingly considering green spaces and bird-friendly architecture to support sparrow habitats. These efforts, grounded in ecological research, aim to create a balanced ecosystem where sparrows can thrive.
Lessons in Resilience
Despite facing numerous ecological challenges, the sparrow's adaptive behaviors and physiological traits exemplify remarkable resilience in fluctuating environments. Their ability to thrive in diverse habitats offers key lessons in resilience.
Sparrows exhibit:
- Metabolic Flexibility: They adjust their metabolic rates, enabling survival during food scarcity.
- Habitat Versatility: Sparrows nest in varied environments, from urban areas to rural landscapes, showcasing ecological adaptability.
- Social Cohesion: They form flocks that enhance foraging efficiency and predator vigilance, critical for survival.
Through detailed observations, one sees that sparrows' resilience stems from their physiological and behavioral adaptations. Understanding these traits provides insight into how species can persist despite environmental pressures.
Their strategies highlight the importance of flexibility and cooperation in nature's survival toolkit.
Sparrows and Human Connection

The intricate bond between humans and sparrows reveals a mutualistic relationship where urbanization paradoxically provides both challenges and opportunities for these resilient birds.
Urban environments offer abundant food sources like discarded crumbs and insects, yet pose threats such as habitat destruction and pollution. Sparrows exhibit remarkable behavioral adaptation, nesting in man-made structures and utilizing anthropogenic resources. However, the decline in green spaces and increased pesticide use adversely affect their populations.
Studies indicate that sparrows benefit from human activities, yet require ecological balance for their survival. Observing their foraging patterns and nesting habits highlights the delicate equilibrium they maintain within human habitats, underscoring the importance of sustainable urban planning to support this enduring avian-human connection.
Encouraging Sparrows in Your Garden
Urban residents seeking to support the sparrow population can employ specific strategies to create a welcoming environment in their own gardens. By addressing their habitat needs, individuals can foster a thriving avian community.
Key actions include:
- Plant Native Vegetation: Native plants provide necessary food sources and nesting materials. They attract insects, an important sparrow diet component, and offer shelter.
- Install Nesting Boxes: Sparrows require secure nesting sites. Installing appropriately sized nesting boxes with a 32mm entrance hole can significantly increase breeding opportunities.
- Provide Fresh Water: A consistent supply of clean water supports hydration and bathing needs. A shallow bird bath with a gentle slope is ideal.
These measures, grounded in ecological principles, create a sustainable habitat conducive to sparrow survival and reproduction.
Conclusion
To sum up, sparrows, with their intricate social structures and rich historical significance, symbolize resilience and interconnectedness. Their melodious communication and presence in literature and art echo the delicate threads of nature's tapestry.
Conservation efforts are essential to maintaining their populations, as sparrows are more than mere birds; they're living proofs of nature's resilience. By encouraging these avian wonders in our gardens, we nurture a deeper connection to the natural world, fostering a symbiotic relationship that benefits all.






