10 Key Differences Between Grasshopper Sparrow Vs Leconte’s Sparrow
Grasshopper Sparrows and LeConte's Sparrows differ significantly in appearance, habitat, and vocalization. Grasshopper Sparrows exhibit buffy tan plumage with a white eye-ring and prefer open grasslands, emitting an insect-like buzz.
In contrast, LeConte's Sparrows display rusty-orange hues with a distinct facial pattern, preferring wetter habitats like marshy meadows and producing melodious whistles. Geographically, Grasshopper Sparrows breed across central and northern U.S., while LeConte's Sparrows nest in the northern Great Plains.
The former's numbers are declining due to habitat loss, whereas the latter's population remains stable. Explore more detailed comparisons for an in-depth understanding of these species.

Key Takeaways
- Grasshopper Sparrows prefer open grasslands, while LeConte's Sparrows favor wetter habitats like marshy meadows.
- Grasshopper Sparrows have buffy, tan plumage with a white eye-ring, contrasting LeConte's Sparrows' rusty-orange hues and distinct facial patterns.
- Grasshopper Sparrows are partial migrants, while LeConte's Sparrows undertake long-distance migrations.
- Grasshopper Sparrows primarily eat insects, especially grasshoppers, whereas LeConte's Sparrows feed on seeds and small invertebrates.
- Grasshopper Sparrows emit insect-like buzzes, while LeConte's Sparrows produce musical whistles and soft trills.
Physical Appearance

When comparing the physical appearance of the Grasshopper Sparrow and LeConte's Sparrow, one immediately notices the distinct coloration and markings that set these species apart. The Grasshopper Sparrow exhibits a buffy, tan plumage with a pale underbelly and a conspicuous white eye-ring. In contrast, LeConte's Sparrow features a more vibrant palette with rich, rusty-orange hues, streaked flanks, and a distinct facial pattern marked by a yellow-brown eyebrow stripe.
Additionally, the Grasshopper Sparrow's crown showcases a subtle, dark central stripe, whereas LeConte's Sparrow's crown is adorned with a sharp, contrasting stripe. These specific markings and color differences provide essential identification cues for ornithologists and bird enthusiasts, making field observations both engaging and informative.
Habitat Preferences
While their physical appearances provide clear identifiers, their habitat preferences offer further distinctions between the Grasshopper Sparrow and LeConte's Sparrow.
The Grasshopper Sparrow favors open grasslands with sparse vegetation, often thriving in grazed pastures and prairies. They're drawn to areas with low, scattered shrubs, utilizing the ground for nesting.
Conversely, LeConte's Sparrow prefers wetter habitats, such as marshy meadows and sedge-dominated wetlands. They seek dense, tall grasses and sedges for nesting, indicating a reliance on more moist environments.
These habitat preferences reflect their differing ecological niches, with Grasshopper Sparrows adapting to drier, open landscapes, while LeConte's Sparrows are tied to wetter, denser vegetation.
Their distinct choices in habitat underscore their unique adaptations and survival strategies.
Geographic Range
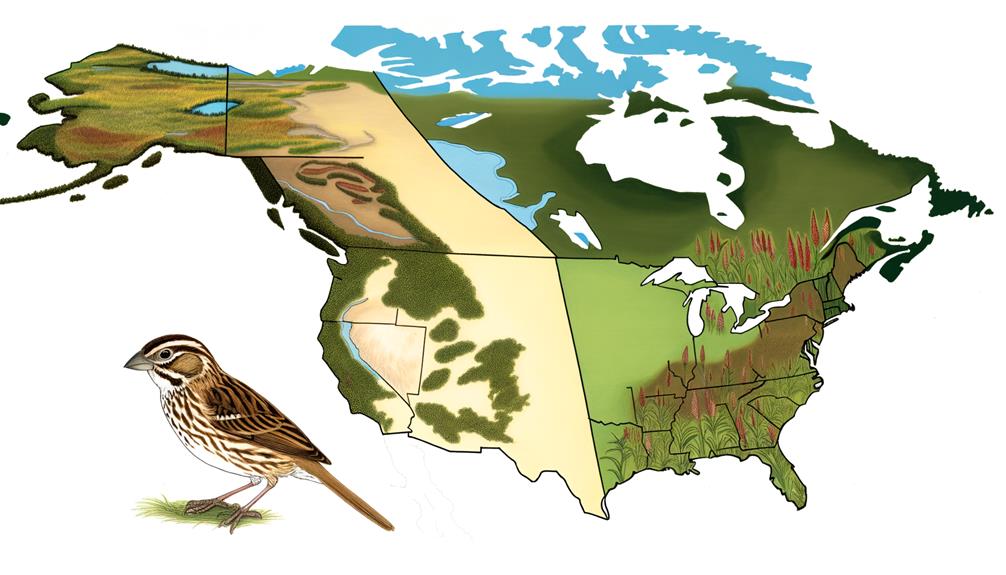
Examining the geographic ranges of Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows reveals notable distinctions in their habitat preferences and migration patterns.
Grasshopper Sparrows mainly inhabit open grasslands across North America, whereas Leconte's Sparrows prefer wetter, marshy environments.
Additionally, both species exhibit differing migratory behaviors, with Grasshopper Sparrows moving shorter distances compared to the longer migrations of Leconte's Sparrows.
Habitat Preferences
Grasshopper Sparrows primarily inhabit open grasslands and prairies, whereas Leconte's Sparrows favor dense, wet meadows and marshlands, highlighting their distinct ecological niches. This habitat divergence underscores their unique adaptations and preferences:
- Grasshopper Sparrows:
- Thrive in well-drained, sparse vegetation.
- Prefer areas with short grasses and minimal woody plants.
- Avoid overly wet or densely vegetated regions.
- Leconte's Sparrows:
- Opt for moist, dense vegetation near wetlands.
- Favor tall grasses and sedges for concealment.
- Require humid environments for breeding success.
These habitat preferences reveal their specific ecological roles and survival strategies, emphasizing the importance of preserving diverse landscapes to support both species.
Their distinct choices reflect evolutionary adaptations to their respective environments, ensuring niche differentiation and coexistence.
Migration Patterns
Both Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows exhibit distinct migration patterns that reflect their adaptation to varying climatic conditions across North America. Grasshopper Sparrows migrate to the southern United States and Mexico during winter, displaying short to medium-distance migratory behavior. Conversely, Leconte's Sparrows undertake longer migrations, traveling from their breeding grounds in the northern Great Plains and Canada to the southeastern United States.
| Species | Migration Pattern |
|---|---|
| Grasshopper Sparrow | Short to medium-distance migration |
| Leconte's Sparrow | Long-distance migration |
| Grasshopper Sparrow | Breeds in central and northern U.S. |
| Leconte's Sparrow | Breeds in northern Great Plains |
| Grasshopper Sparrow | Winters in southern U.S. and Mexico |
| Leconte's Sparrow | Winters in southeastern U.S. |
These migration patterns underscore their ecological niches and the environmental pressures shaping their life cycles.
Feeding Habits
How do the distinct feeding habits of Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows reflect their adaptations to different ecological niches?
Grasshopper Sparrows primarily consume insects, particularly grasshoppers, which they capture in grassy fields, showcasing their adaptation to open habitats.
Leconte's Sparrows, on the other hand, primarily feed on seeds and small invertebrates in wet meadows, reflecting their preference for more humid environments.
Grasshopper Sparrows:
- Diet: Insects, especially grasshoppers.
- Preferred Habitat: Open grassy fields.
- Foraging Technique: Ground foraging.
Leconte's Sparrows:
- Diet: Seeds, small invertebrates.
- Preferred Habitat: Wet meadows.
- Foraging Technique: Low vegetation exploration.
These dietary distinctions illustrate their specialized feeding strategies and ecological adaptations.
Vocalizations

In addition to their distinct feeding habits, the vocalizations of Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows further highlight their unique adaptations to their respective habitats. Grasshopper Sparrows emit a distinctive, insect-like buzz that blends seamlessly with the sounds of open grasslands, offering a camouflage effect against predators. Their song consists of a high-pitched 'tik' followed by a rapid trill.
Conversely, Leconte's Sparrows produce a more musical, melodious series of whistles interspersed with soft trills, which serve to communicate effectively within dense grasslands and marshes. These vocal differences not only facilitate territory establishment and mate attraction but also underscore the evolutionary divergence shaped by their environments.
Both species' calls reflect intricate adaptations essential for survival and communication.
Breeding Behavior
Breeding behavior in Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows exhibits distinct patterns influenced by their respective habitats. Grasshopper Sparrows construct simple ground nests in open grasslands, while Leconte's Sparrows opt for well-concealed nests within dense vegetation.
Grasshopper Sparrows demonstrate monogamous pair bonds and exhibit conspicuous territorial displays. In contrast, Leconte's Sparrows engage in polygynous behavior and display less overt territoriality.
Key comparative observations include:
- Mating Systems: Grasshopper Sparrows are monogamous, while Leconte's Sparrows are often polygynous.
- Nesting Strategy: Grasshopper Sparrows prefer open areas; Leconte's Sparrows favor dense cover.
- Territorial Behavior: Grasshopper Sparrows show more territorial aggression.
- Parental Roles: Both species share parental duties, but the specifics vary with habitat demands.
These differences highlight their adaptive strategies to distinct environments.
Nesting Sites
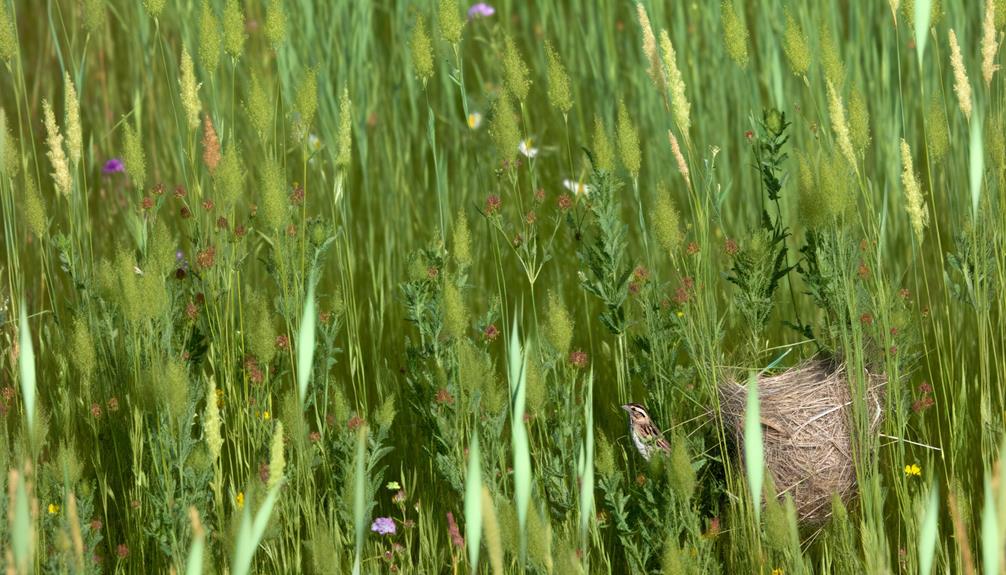

Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows select nesting sites that reflect their adaptations to differing habitats, with Grasshopper Sparrows often choosing open grasslands and Leconte's Sparrows favoring dense, vegetative cover.
Grasshopper Sparrows typically nest on the ground, constructing shallow, cup-shaped nests amidst grasses. Their preference for open areas allows for easier predator detection.
In contrast, Leconte's Sparrows build nests in wetter, marshy environments with abundant vegetation. They often anchor their nests to plant stems above the ground, providing protection from flooding and concealment from predators.
This comparative nesting strategy highlights their ecological divergence. Each species' nesting behavior ensures maximum reproductive success by exploiting habitat-specific resources, demonstrating evolutionary adaptations finely tuned to their respective environments.
Migration Patterns
While their nesting sites reflect distinct ecological adaptations, their migration patterns further underline the differences in their life strategies.
Grasshopper Sparrows exhibit partial migratory behavior, with northern populations moving to southern U.S. and Mexico, while some southern populations remain year-round.
In contrast, Leconte's Sparrows are long-distance migrants, traveling from breeding grounds in Canada and the northern U.S. to wintering habitats in the southeastern U.S.
To summarize their migration patterns:
- Grasshopper Sparrows:
- Partial migratory behavior
- Northern populations migrate south
- Some southern populations are sedentary
- Leconte's Sparrows:
- Long-distance migration
- Breeding in Canada/northern U.S.
- Wintering in southeastern U.S.
These divergent strategies reflect their unique adaptations to environmental pressures and resource availability.
Population Status

Current population trends indicate that Grasshopper Sparrow numbers have been declining markedly due to habitat loss, whereas Leconte's Sparrow populations have remained relatively stable.
Both species benefit from targeted conservation efforts, but Grasshopper Sparrows require more immediate intervention to halt their decline.
Comparative analysis of these trends highlights the varying effectiveness of conservation strategies across different habitats and regions.
Current Population Trends
Recent surveys indicate contrasting population trends for Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows, highlighting significant differences in their conservation status. Grasshopper Sparrows exhibit a declining trend, attributed to habitat loss and degradation.
In contrast, Leconte's Sparrows show stable or slightly increasing numbers, likely benefiting from conservation measures and habitat management.
Grasshopper Sparrow Decline: Their numbers have decreased by over 30% in the last decade, primarily due to agricultural expansion.
Leconte's Sparrow Stability: Their population remains relatively stable, with slight increases noted in managed grasslands.
Habitat Preferences: Grasshopper Sparrows prefer open grasslands, while Leconte's Sparrows thrive in wetter, marshy areas.
Geographic Distribution: Grasshopper Sparrows are widespread across North America, whereas Leconte's Sparrows have a more limited range.
Conservation Efforts Impact
Effective conservation efforts have played a pivotal role in stabilizing the population of Leconte's Sparrows, contrasting sharply with the continued decline of Grasshopper Sparrows.
Leconte's Sparrows have benefited from targeted habitat restoration and management practices, including controlled burns and wetland preservation. These measures have enhanced their breeding and foraging habitats, resulting in a steady population trend.
Conversely, Grasshopper Sparrows haven't experienced the same success. Despite some conservation initiatives, their habitats remain fragmented due to agricultural expansion and urbanization. The lack of large-scale, coordinated efforts has exacerbated their decline.
Comparative analysis reveals that species-specific strategies and habitat continuity are vital for effective conservation, underscoring the need for more robust initiatives for Grasshopper Sparrows.
Predators and Threats
Identifying the primary predators of the Grasshopper Sparrow and Leconte's Sparrow reveals significant differences in their ecological challenges. Grasshopper Sparrows face threats mainly from terrestrial predators, while Leconte's Sparrows are more vulnerable to avian predators due to their habitat preferences. Both species experience predation from similar sources, but the intensity and type of predation vary.
Key threats include:
- Mammalian Predators: Coyotes, raccoons, and domestic cats pose significant risks to Grasshopper Sparrows.
- Avian Predators: Hawks, owls, and shrikes frequently target Leconte's Sparrows.
- Habitat Loss: Agricultural expansion and urban development reduce nesting sites for both species.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns and increased frequency of extreme events affect food availability and nesting success.
These distinctions highlight the varied ecological pressures shaping their survival.
Conservation Efforts

Acknowledging the distinctive challenges faced by Grasshopper Sparrows and Leconte's Sparrows, conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration, predator control, and climate resilience strategies tailored to each species' specific needs.
Grasshopper Sparrows benefit from prairie restoration projects that promote native grasses, while Leconte's Sparrows thrive in wetland management programs enhancing sedge and cattail growth.
Predator control measures, such as installing predator exclusion devices, mitigate nest predation risks for both species. Climate resilience strategies incorporate adaptive management practices, including controlled burns and water level regulation, to maintain ideal breeding environments.
Comparative analysis reveals that while both species require habitat-specific interventions, Grasshopper Sparrows are more reliant on open grasslands, whereas Leconte's Sparrows depend on wetter, marsh-like habitats for survival.
Birdwatching Tips
Birdwatchers should focus on identifying key morphological differences, such as the Grasshopper Sparrow's distinctively short tail and the Leconte's Sparrow's more vivid coloration.
Best viewing times for both species are during the early morning hours when they're most active.
Essential gear for this endeavor includes binoculars with high magnification, a field guide for quick reference, and a notebook for recording observations.
Identifying Key Features
When distinguishing between the Grasshopper Sparrow and Leconte's Sparrow, one should closely examine their head patterns and coloration, as these features provide reliable identification markers.
The Grasshopper Sparrow exhibits a flat head with a distinct, pale central crown stripe and an overall buffy appearance. In contrast, Leconte's Sparrow shows a more rounded head with a pronounced dark crown and a striking, bright yellowish-orange face.
Here are key features to observe:
- Head Pattern: Grasshopper Sparrow has a pale central crown stripe, while Leconte's Sparrow has a dark crown.
- Face Coloration: Grasshopper Sparrow's face is buffy; Leconte's Sparrow features a yellowish-orange face.
- Overall Body Color: Grasshopper Sparrow appears more uniformly buffy.
- Tail Characteristics: Grasshopper Sparrow has a shorter, more squared tail compared to Leconte's Sparrow.
Optimal Viewing Times
To maximize the chances of observing both Grasshopper and Leconte's Sparrows, early morning hours, particularly around dawn, provide the best lighting and activity levels for these species. During this period, Grasshopper Sparrows tend to sing more frequently, making them easier to locate through their distinctive buzzing calls.
In contrast, Leconte's Sparrows exhibit heightened foraging activity, often moving through dense grasses. Observers should note that overcast mornings can extend the most favorable viewing time by reducing harsh shadows, thereby enhancing visibility. The comparative advantage lies in the lighting conditions; dawn's soft light accentuates the subtle field marks distinguishing these sparrows.
Birdwatchers seeking freedom in nature will find dawn excursions both rewarding and enriching, enhancing their chances for successful identification and observation.
Essential Gear Checklist
Equipped with the right tools, observers can greatly enhance their birdwatching experience and accuracy in identifying Grasshopper and Leconte's Sparrows. Precision equipment aids in distinguishing subtle differences in plumage and behavior.
Essential gear includes:
- High-Quality Binoculars: Essential for observing fine details such as the Grasshopper Sparrow's buffy eye-ring versus Leconte's Sparrow's white crown stripe.
- Field Guide: A thorough guide helps compare field marks and song patterns, fostering more accurate identification.
- Notebook and Pen: Crucial for recording behavioral observations and distinguishing characteristics, enabling a more detailed comparative analysis.
- Camera with Zoom Lens: Captures high-resolution images, allowing for post-observation scrutiny and sharing findings with fellow birdwatchers.
These tools empower enthusiasts to explore with precision and freedom.
Conclusion
In the intricate dance of avian life, Grasshopper Sparrows and LeConte's Sparrows showcase distinct yet overlapping niches. While one thrives in open grasslands and the other in marshy habitats, both face common threats from habitat loss and predation.
Conservation efforts must be nuanced, addressing specific ecological needs. Birdwatchers, attuned to their unique calls and behaviors, can play a pivotal role in monitoring populations.
Ultimately, preserving these sparrows echoes the broader imperative of safeguarding biodiversity.






