The Art of How Sparrows Do Attach Their Nests to Cliffs
Sparrows attach their nests to cliffs through a meticulous process. You'll see them selecting stable cliff faces with crevices and indentations, often preferring south-facing sites for warmth.
They gather lightweight, durable materials like grasses, twigs, and feathers for nest construction. For adhesion, sparrows mix fine mud, saliva, and plant fibers, creating a strong binding agent.
You'll find nests carefully placed in natural depressions or ledges to enhance stability. Field studies show they usually avoid areas with high human activity and opt for cliffs with minimal erosion, ensuring their nests stay secure through varying weather conditions.
Discover the intricacies behind their remarkable nesting techniques.

Key Takeaways
- Sparrows use mud, saliva, and plant fibers as natural adhesives to attach nests to cliff faces.
- Fine mud particles are moistened to form a binding agent for nest adhesion.
- Natural anchor points and increased surface area on cliffs aid in nest attachment.
- Sparrows select cliffs with minimal erosion to ensure stability and grip for their nests.
- The porosity and rough texture of preferred rocks like limestone and sandstone enhance nest adherence.
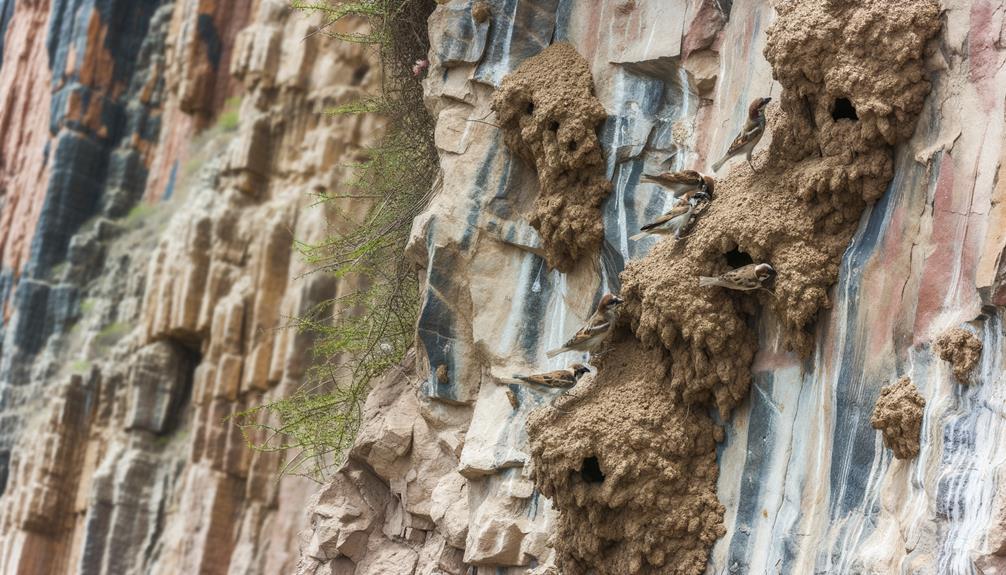
Site Selection
When selecting a nesting site, sparrows carefully evaluate different cliff faces to guarantee ideal safety and proximity to food sources. You'll observe these birds meticulously inspecting potential sites, analyzing factors like the stability of the cliff, absence of predators, and the availability of nearby vegetation or insects.
Field studies show that sparrows often choose south-facing cliffs, which provide warmth and protection from harsh weather. They also prefer areas with minimal human activity, reducing the risk of disturbance.
Nesting Materials
When observing sparrows building nests on cliffs, you'll notice they primarily use grasses, twigs, and feathers.
Field studies reveal that these birds exhibit a meticulous material selection process, often opting for lightweight yet durable components.
Common Nesting Materials
Field studies reveal that sparrows mainly use grasses, twigs, and feathers as the primary materials for constructing their nests.
You'll find that these birds select specific types of grasses and twigs that provide structural integrity and flexibility.
Feathers are incorporated to add insulation and comfort.
Observations indicate that sparrows prefer dry, sturdy grasses that can be easily woven together.
Smaller twigs are used to create a robust framework, ensuring the nest adheres securely to cliff faces.
Feathers often come from other birds or are collected from the environment, providing a soft lining.
Material Selection Process
During nest construction, sparrows meticulously evaluate and select each material based on its structural properties and availability. You'll observe that they prefer sturdy twigs for the foundation, ensuring stability against the wind. Grass and leaves often form the nest's softer interior, providing insulation and comfort for their eggs. Mud is another essential component; sparrows use it like cement to bind the nest to the cliff face securely.
Field studies reveal sparrows' impressive adaptability: they'll incorporate human-made materials like string and paper when natural options are scarce. This resourcefulness highlights their ability to thrive in various environments. By understanding their material selection process, you can better support these birds, ensuring their nesting sites are safe and conducive to their needs.
Cliff Surface Analysis
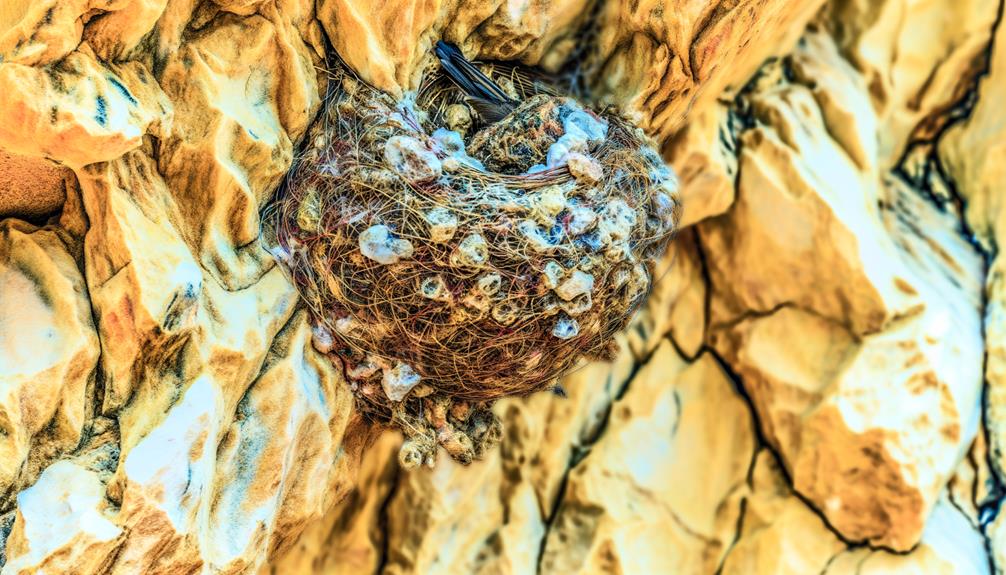

The cliff's surface, characterized by its rugged texture and varied mineral composition, plays an important role in the sparrows' nest attachment process.
You'll notice that sparrows prefer cliffs with numerous crevices and indentations. These features provide natural anchor points and increased surface area for nest materials to adhere.
Field studies reveal that cliffs rich in quartz and feldspar offer ideal nesting conditions due to their roughness and durability.
You can observe that sparrows often choose sites with minimal erosion, ensuring stability. Additionally, the presence of lichen and moss can enhance grip, aiding in nest adherence.
Structural Design
Understanding the structural design of sparrow nests reveals intricate construction techniques that guarantee both stability and protection. Sparrows use a combination of twigs, grasses, and feathers, woven meticulously to form a compact, resilient structure. Field studies show that these materials are strategically selected for their tensile strength and flexibility.
Sparrows craft the outer layers with sturdier twigs, creating a solid framework, while the inner layers are lined with softer materials for insulation and comfort. Observations indicate that sparrows incorporate natural depressions and ledges on cliff faces into their nest architecture, enhancing stability. This design not only protects the nest from wind and rain but also keeps predators at bay.
Your understanding of these techniques can inspire more effective conservation practices.
Adhesion Techniques
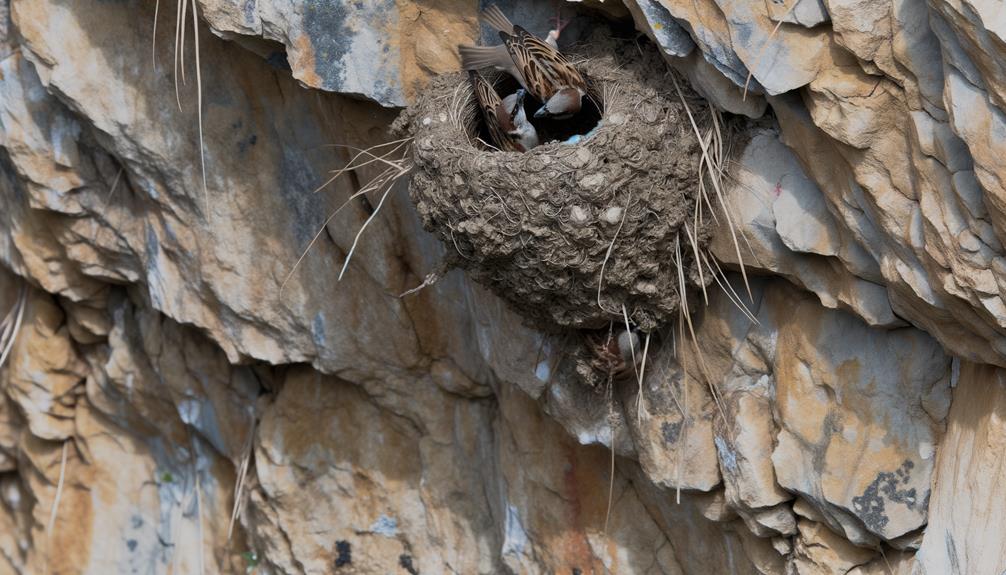

You'll observe that sparrows use a combination of mud, saliva, and plant fibers to enhance the adhesion of their nests to cliff faces.
Field studies reveal that these natural nesting materials offer both flexibility and strength, important for withstanding environmental stressors like wind and rain.
These adaptations guarantee the nests remain securely attached, safeguarding the sparrows' offspring.
Natural Nesting Materials
Many sparrows utilize a unique combination of mud, grasses, and plant fibers to create a strong adhesive for securing their nests to cliff faces.
You'll observe that sparrows first gather fine mud particles, ensuring it's moist enough to provide a binding agent. Then, they meticulously weave grasses and plant fibers into this mud matrix.
Field studies indicate that this mixture increases the nest's structural integrity, making it resilient against winds and gravity. By integrating these natural materials, sparrows achieve a balance of flexibility and strength.
This method allows them to serve their offspring by providing a stable and secure environment. Your commitment to understanding these techniques can aid in conserving their habitats and supporting their nesting success.
Environmental Adaptations
Sparrows frequently employ a sophisticated set of adhesion techniques to secure their nests to cliff faces, optimizing their survival in harsh environments. You'll observe that these birds meticulously gather a combination of mud, saliva, and plant fibers, creating a powerful adhesive.
Field studies show that sparrows often select nesting sites with small crevices and ledges, providing additional structural support. Their skillful use of natural resources and strategic site selection reduces the risk of nest detachment due to wind or rain.
You can appreciate how sparrows continuously adapt these methods based on environmental conditions, demonstrating remarkable ingenuity and resilience. Their ability to engineer stable nests on precarious cliffs is a proof of their evolutionary success in challenging habitats.
Use of Saliva
Observing sparrows closely reveals that they ingeniously use their saliva as a natural adhesive to anchor their nests firmly to cliff faces.
During your field studies, you'll notice that sparrows gather small twigs, grass, and feathers. They then moisten these materials with their saliva, which acts as an effective binder.
This behavior ensures that the nest components stick together securely, even in adverse weather conditions. When you watch sparrows in action, you'll see how they meticulously apply their saliva to each piece, creating a robust structure.
This method not only provides stability but also demonstrates the sparrows' remarkable adaptation to their environment. By comprehending this process, you can better appreciate the sparrows' resourcefulness and the delicate balance of nature they maintain.
Nest Anchoring
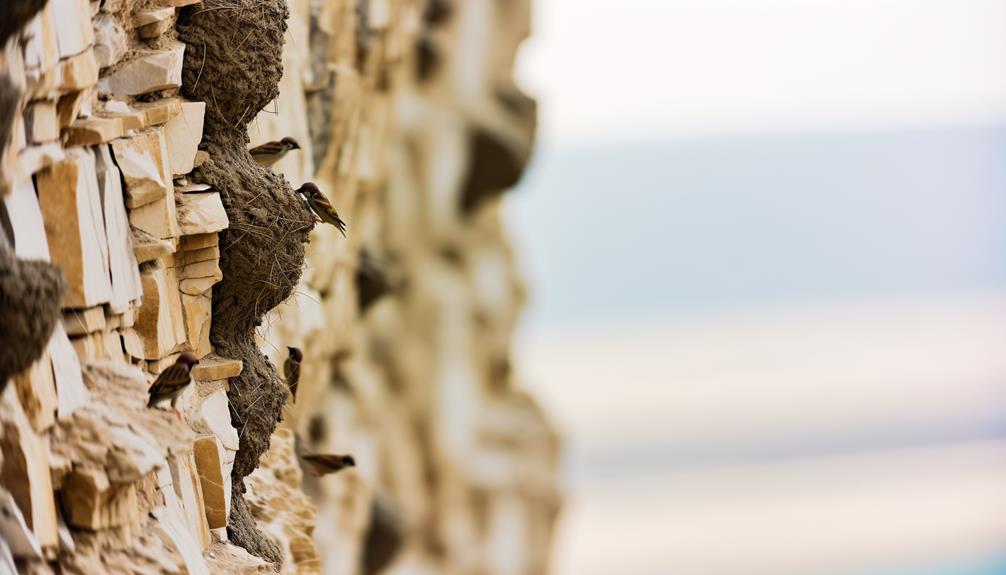

When examining the anchoring mechanisms of sparrow nests on cliff faces, you'll observe that these birds expertly intertwine twigs and grasses into natural crevices, enhancing structural stability. Through detailed field studies, several anchoring strategies have been documented:
- Interweaving Materials: Sparrows use a combination of twigs, grasses, and other plant materials, securely interlocking them to form a robust base.
- Utilizing Crevices: Natural fissures in the rock provide ideal points for nest attachment, allowing sparrows to wedge materials tightly.
- Saliva as Adhesive: Sparrows often use their saliva to bind materials together, reinforcing the nest's overall integrity.
Environmental Factors
When observing sparrows' nesting habits, you should focus on environmental factors such as cliff material preferences, which influence nest attachment.
Field studies reveal that wind and weather have a major impact on nest stability and survival.
Additionally, vegetation and natural shelter play important roles in providing protection and support for these cliffside structures.
Cliff Material Preferences
Sparrows show a marked preference for cliffs composed of limestone and sandstone, as these materials provide ideal conditions for nest attachment and stability.
Field studies have shown that limestone and sandstone cliffs offer several advantages:
- Porosity: These rocks are porous, allowing sparrows to weave their nest materials securely.
- Surface Texture: The rough texture of these cliffs helps nests adhere better, reducing the risk of them falling.
- Thermal Properties: These materials can moderate temperature fluctuations, providing a stable environment for eggs and chicks.
Wind and Weather Impact
While sparrows favor limestone and sandstone cliffs for their porosity and texture, environmental factors like wind and weather play a significant role in the success of nest attachment. You'd observe that strong, consistent winds can dislodge nests if they're not securely anchored. Rain and humidity can erode cliff surfaces, impacting the adhesion of nests. Field studies indicate that sparrows often choose less exposed cliff faces to mitigate these risks.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on Nest Attachment |
|---|---|
| Wind | Dislodges nests |
| Rain | Erodes cliff surfaces |
| Humidity | Weakens nest adhesion |
| Temperature | Affects nesting materials |
Vegetation and Shelter
Nest placement on cliffs is often influenced by the availability of vegetation, which provides additional shelter and camouflage. You can observe sparrows selecting sites with abundant plant life, as it offers several advantages:
- Protection from Predators: Dense foliage hides nests from predators.
- Climate Moderation: Vegetation helps regulate temperature and humidity.
- Structural Support: Plants can physically support nest construction.
Field studies show that sparrows prefer cliff faces with shrubs, grasses, or mosses. These natural elements act as both a shield and a stabilizing structure for nests. By choosing such locations, sparrows enhance their survival chances.
You can see how they adeptly utilize their environment, aligning nest placement with the availability of protective vegetation.
Predator Avoidance
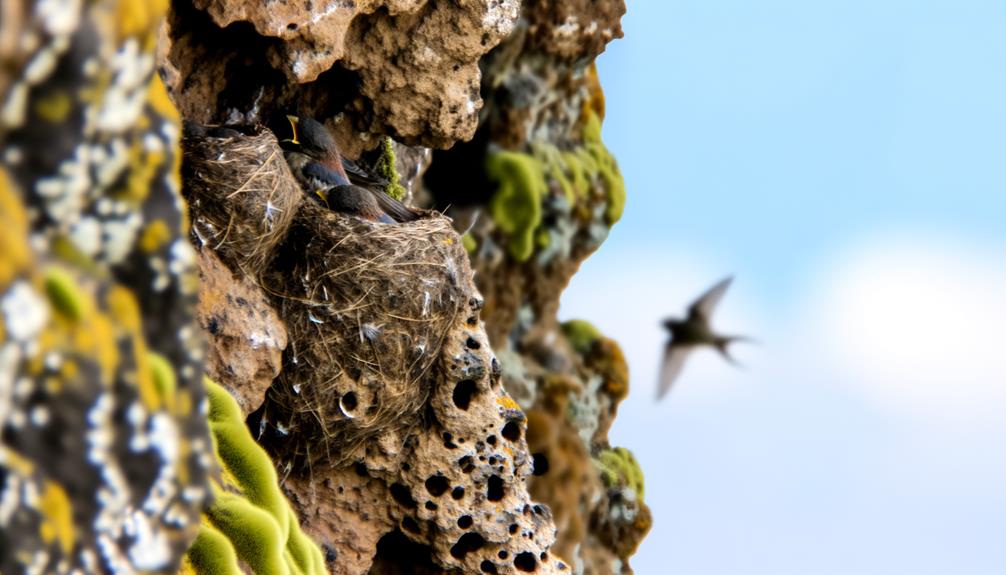

Many sparrow species cleverly choose cliff faces to nest on, greatly reducing their vulnerability to ground-based predators. You'll find that this strategic location makes it difficult for mammals and snakes to access the nests.
Field studies reveal that sparrows prefer sheer, vertical surfaces, minimizing exposure to predators. Observations indicate that these birds exhibit heightened vigilance, often selecting nesting sites with minimal ledges, further complicating predator access.
By choosing these hard-to-reach spots, sparrows effectively safeguard their eggs and chicks. This behavior demonstrates a sophisticated understanding of their environment, ensuring the survival of the next generation.
Your role in observing and documenting these behaviors helps enhance our collective knowledge, ultimately aiding in the conservation efforts for these remarkable birds.
Adaptation and Evolution
The sparrows' preference for nesting on cliffs is a result of evolutionary adaptations that have honed their ability to exploit these challenging environments for survival.
Your observations in the field might reveal several key adaptations that make cliff nesting viable:
- Foot Structure: Sparrows have developed strong, agile feet that allow them to grip rocky surfaces securely.
- Nest Construction: Their nests are built with materials that bind well to the cliff face, such as mud and plant fibers.
- Flight Agility: These birds exhibit enhanced maneuverability, enabling them to navigate the complex cliff terrain skillfully.
Conclusion
In observing sparrows' cliffside nesting, you've seen their fascinating adaptation and ingenuity. These birds meticulously select sites, gather materials, and utilize unique adhesion techniques to guarantee nest stability.
Imagine sparrows, nature's engineers, anchoring their homes against gravity's pull. Their strategic choices mitigate environmental factors and predator threats. This intricate behavior highlights evolution's role in shaping survival strategies.
Your field studies reaffirm that even the smallest creatures exhibit remarkable resilience and intelligence in their quest for survival.






